Tachograph – country codes and important designations
3 April '25
Reading time 6 minutes
Do you know how important tachographs are for truck drivers and the wider international transport industry? These devices don’t just record working time — they’re also a key part of transport documentation. That makes them absolutely essential for logistics operations.
Among the many details recorded by a tachograph are country codes, which indicate where a driver was located at a given time. These codes are extremely important and missing or incorrect entries can lead to serious consequences.
The obligation to enter country codes applies to every border crossing of an EU member state. The code must be entered at the nearest possible stopping point and in newer tachographs this happens automatically.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at how country codes work in tachographs, why they matter and what the consequences are for using them incorrectly.
Table of contents
Country codes in tachographs – full list
Penalties for failing to record country codes
What is a tachograph?
A tachograph is a device mainly used in heavy-duty vehicles that records drivers’ working hours, speed and mileage. Digital tachographs are one of the primary tools used to ensure compliance with transport regulations.

The latest rules regarding digital tachographs are set out in the Mobility Package, which came into effect in 2020 under EU law. It introduced several new requirements for the international road transport industry.
One of the main goals of the Mobility Package is to ensure that transport operations across the EU comply with regulations concerning drivers’ working hours, helping to prevent fatigue. This is an important step toward improving road safety.
The Mobility Package also regulates how digital or analogue tachographs must be used — including the requirement to record the country symbols representing the countries through which the vehicle is travelling.
Country codes on the tachograph
One of the key elements recorded by a tachograph is the country code. Every driver crossing the border of an EU member state must enter the code of the country they are in. This allows for precise tracking of the route and helps determine where and when a driver entered a particular country.
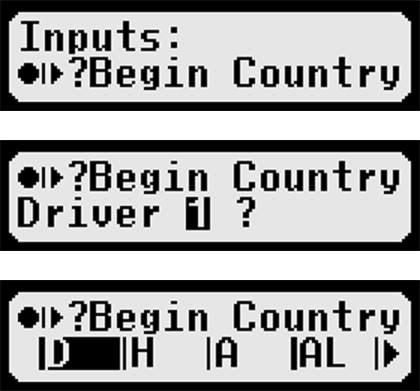
Country codes in the tachograph are essential for maintaining accurate vehicle documentation. At the end of a daily work period, the driver must ensure that all country codes have been entered correctly.
What country codes are used in tachographs?
In Europe, tachographs use one-, two-, or three-letter codes that are unique to each country. Entering the code after crossing a border is a required part of properly documenting a trip.

Country codes in the tachograph
Drivers must enter country codes into the digital smart tachograph immediately after crossing into another EU member state. This is essential for accurate route tracking and compliance with regulations, including those new rules outlined in the Mobility Package.
Newer tachographs make this task easier by automatically recording data – such as the country codes of the states being traveled through.
Automatic country registration in the tachograph
New smart tachos are equipped with GPS systems that automatically detect and record country changes based on current geographic data. This eliminates the need for manual input by the driver and significantly reduces the risk of errors. The system is more accurate and helps avoid accidental omissions of required country codes.

However, when a driver crosses a country’s border, they should check after crossing whether the code has been correctly recorded. This ensures that the data stored on their personal driver card and in the tachograph memory is accurate.
Country codes in the digital tachograph – country symbols
These codes are official one-, two-, or three-letter abbreviations of country names. Depending on the version of the tachograph used, the driver either manually enters the country symbol from the list below after crossing a border, or the country code is changed automatically. According to regulations, manual entry of the country code must be done at the nearest possible stopping point.
A – Austria
AL – Albania
AND – Andorra
ARM – Armenia
AZ – Azerbaijan

B – Belgium
BG – Bulgaria
BIH – Bosnia and Herzegovina
BY – Belarus

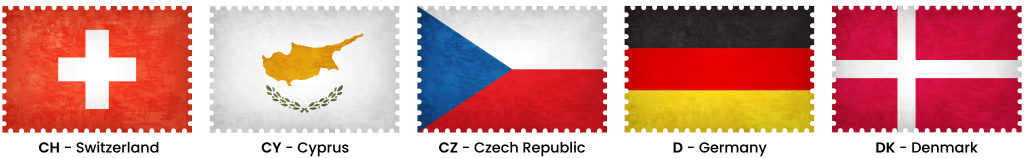
CH – Switzerland
CY – Cyprus
CZ – Czech Republic
D – Germany
DK – Denmark
E – Spain
EST – Estonia
EC – European Community / European Union

F – France
FIN – Finland
FL – Lichtenstein
FO – Faroe Islands

GE – Georgia
GR – Greece
H – Hungary
HR – Croatia

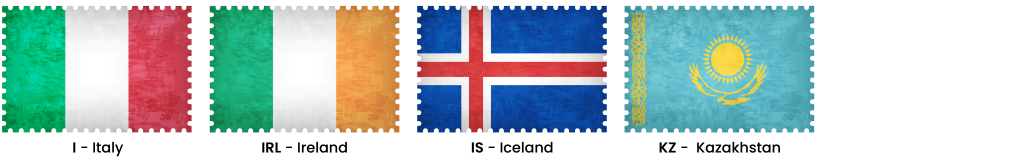
I – Italy
IRL – Ireland
IS – Iceland
KZ – Kazakhstan
L – Luxembourg
LT – Lithuania
LV – Latvia

M – Malta
MC – Monaco
MD – Moldova
MK – North Macedonia
MNE – Montenegro

N – Norway
NL – Netherlands
P – Portugal
PL – Poland

RO – Romania
RSM – San Marino
RUS – Russia

S – Sweden
SK – Slovakia
SLO – Slovenia
SRB – Serbia

TR – Turkey
UA – Ukraine
UK – United Kingdom
WLD – Other countries of the world
V – Vatican

Above codes are used to indicate which country the driver is currently in or was in at a given time. This information is essential for verifying whether the end of a work period complies with the legal requirements of the respective country.
Why are correct country codes on the tachograph important when crossing a border?
Errors in entered nation codes – or a complete lack of them – can lead to serious consequences. Road inspections across various countries require the tachograph to be fully completed with all the necessary data.

If this requirement is not met, both the driver and the transport company are usually subject to financial penalties, which can impact the company’s operations. Entering the correct country code is a key obligation that helps avoid significant fines.
Try HOGS Maps totally free for 14 days!
Fines for missing country codes in the tachograph
Fines for missing or incorrect country codes can be severe. Depending on the country, penalties imposed by control authorities may range from several hundred to several thousand euros.
For example:
- In Germany, the fine can reach up to €250 for the driver and up to €750 for the transport company.
- In Spain, failure to enter the correct code may result in a fine of up to €1,000.
Summary
Correctly entering country codes in the tachograph is essential for staying compliant with road transport regulations. Both drivers and transport companies must ensure the accuracy of this data to avoid strict penalties and inspection issues.
Whether you’re using a manual or automatic system, understanding and applying country codes is fundamental for efficient and smooth transport operations. Drivers are responsible for entering the country code when crossing an EU border and at the end of each daily work period, in line with legal requirements. They must consistently ensure that the digital tachograph contains all necessary information.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How to enter the country code in a tachograph?
Entering a country code in a tachograph depends on the model of the device. In older tachographs, you need to manually select the appropriate country from the device menu and enter its one-, two- or three-letter code (e.g., PL for Poland).
In newer tachographs equipped with GPS, the country code may be registered automatically. However, after crossing a border into a new country, it’s always recommended to verify whether the code has been correctly recorded at the point of entry.
During a roadside inspection, missing this entry may result in financial penalties.
What are the regional codes in Spain?
Spain is the only country in Europe where, in addition to the country code “E” (Spain), drivers are also required to enter a regional code — but only in two specific cases.
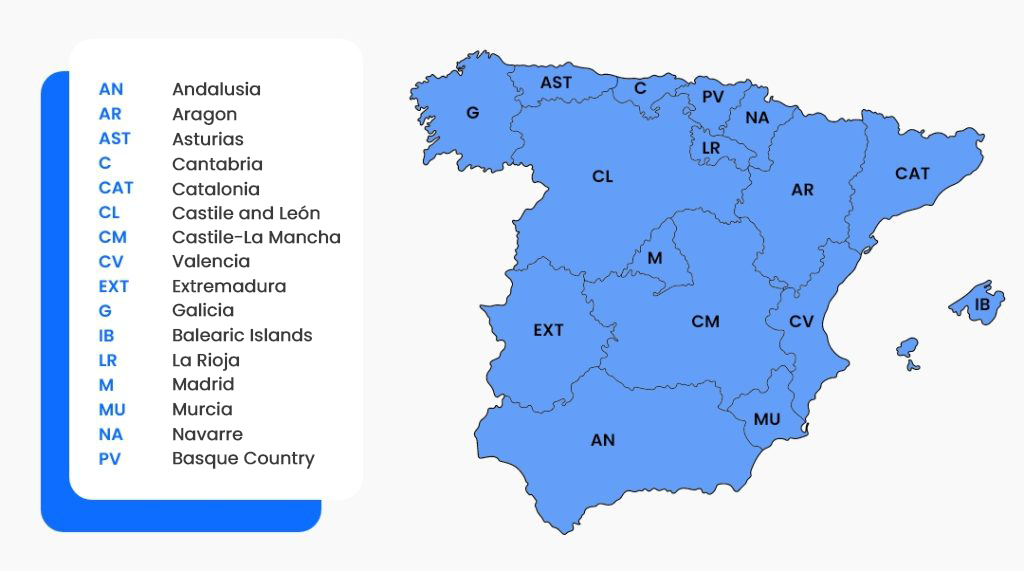
When crossing the Spanish border as part of an international route, transport drivers only need to enter the country code “E”. However, if the vehicle starts or ends its route within Spain, the driver is also required to enter the specific regional code corresponding to the area of departure or arrival.
Spain’s regional codes:
| Region Code | Region |
|---|---|
| AN | Andalusia |
| AR | Aragon |
| AST | Asturias |
| C | Cantabria |
| CAT | Catalonia |
| CL | Castile and León |
| CM | Castile-La Mancha |
| CV | Valencia |
| EXT | Extremadura |
| G | Galicia |
| IB | Balearic Islands |
| IC | Canary Islands |
| LR | La Rioja |
| M | Madrid |
| MU | Murcia |
| NA | Navarre |
| PV | Basque Country |
What is the tachograph abbreviation for Luxembourg?
The abbreviation for Luxembourg in the tachograph is L.
What is the abbreviation for France?
The abbreviation for France in the tachograph is F.
What is the designation for Spain in the tachograph?
Spain in the tachograph has the country code E.

